GMT Compression Molding Technology: Process, Advantages, and Applications
GMT (Glass Mat Thermoplastics) compression molding is a composite material forming process that combines glass fibers and thermoplastics. This process involves heating the composite material to a high temperature and then applying pressure to mold it. It is widely used in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and construction. With the increasing demand for lightweight materials, GMT compression molding plays a crucial role in modern manufacturing.
I. Overview of GMT Compression Molding
GMT compression molding technology combines high-performance thermoplastic resins with glass fibers to create composite materials with extremely high strength, corrosion resistance, and high-temperature resistance. These excellent properties make it an ideal choice in many applications, especially where high strength and low weight are required. This technology enables the efficient manufacturing of complex parts using precision molding equipment and is widely used in fields such as automotive, aerospace, and construction, meeting the demands of modern industry for high-performance materials.
II. The Process Flow of GMT Compression Molding
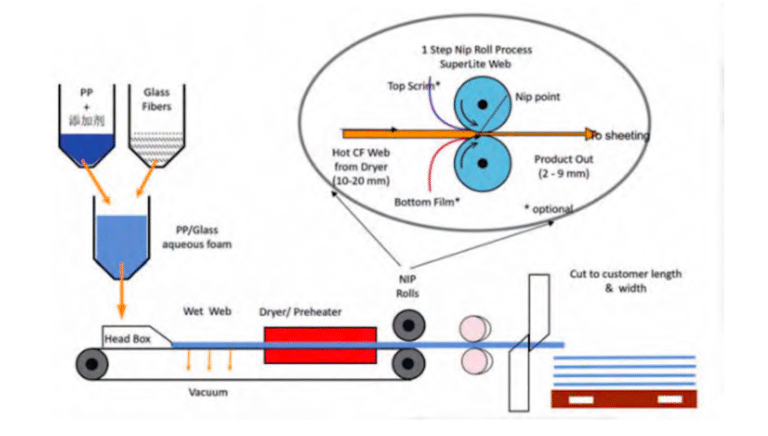
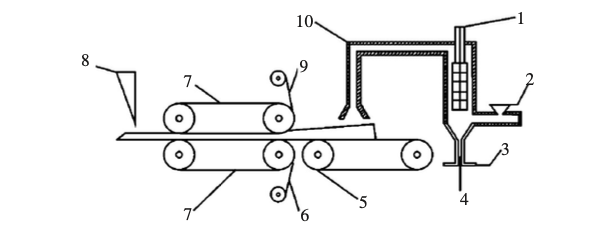
The basic process flow of GMT compression molding includes the following steps:
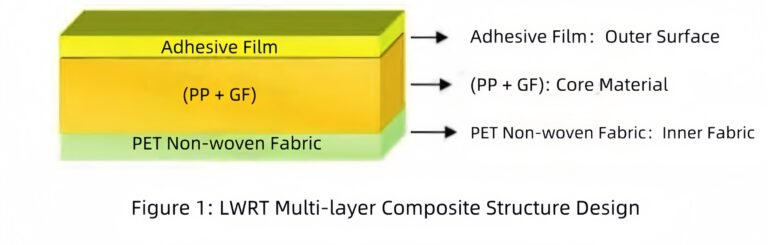
- Material Preparation: Selecting a suitable GMT composite material, typically composed of glass fibers and a thermoplastic resin (such as PP, PE, etc.), which offers high strength and durability.
- Heating: The composite material is heated to a specific temperature to soften it, facilitating the subsequent molding process.
- Compression Molding: The heated material is placed into a mold, and pressure is applied to shape the material, completing the initial forming.
- Cooling and Demolding: After the part has been formed, it is cooled to room temperature and then removed from the mold to obtain the desired component shape.
- Post-processing: The demolded part undergoes trimming, surface treatment, and other finishing processes to meet the final quality standards.
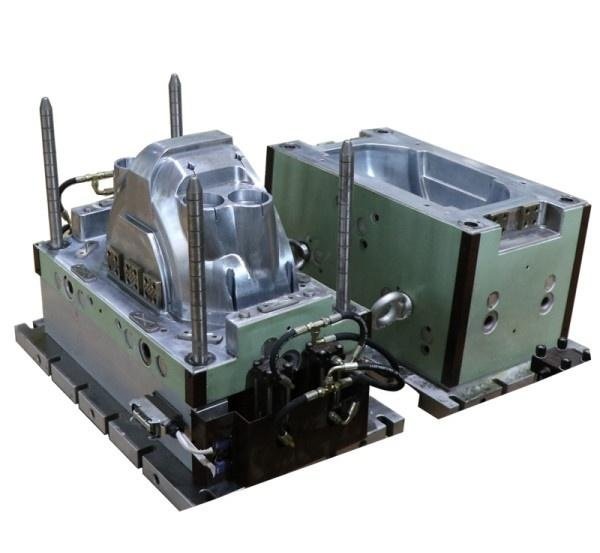

III. Advantages of GMT Compression Molding
Compared to traditional material processes, GMT compression molding technology offers several distinct advantages:
- Lightweight Design: The density of GMT material is much lower than that of metal, making parts manufactured from it significantly lighter than traditional metal parts. This reduces overall weight and decreases energy consumption.
- High Strength and High Rigidity: Reinforced with glass fibers, GMT materials possess excellent mechanical strength and rigidity, enabling them to withstand significant loads and pressures.
- Excellent Corrosion and High-Temperature Resistance: GMT materials perform exceptionally well in harsh environments, especially in high-temperature and corrosive conditions, offering a longer service life than traditional metal materials.
- Electrical Properties: GMT materials have good electrical insulation properties, making them suitable for the production of components for electrical and electronic equipment.
- Efficient Production: The process has a short production cycle, making it suitable for large-scale production while also reducing manufacturing costs.
IV. Application Areas of GMT Compression Molding
Due to its lightweight and high-strength characteristics, GMT compression molding technology is widely used in the following industries:
- Automotive Industry: GMT materials are extensively used for automotive parts such as body panels, bumpers, and door frames, helping to achieve vehicle lightweighting and improve performance and fuel efficiency.
- Aerospace: The aerospace industry has extremely high requirements for lightweight and high-strength materials. GMT compression molding technology provides high-performance materials that meet these needs and is widely used for aircraft interiors, structural components, and more.
- Construction Industry: In the construction industry, GMT materials are used for exterior wall panels, roofing, and flooring components, offering excellent corrosion and high-temperature resistance suitable for various harsh climate conditions.
- Home Appliance Industry: The housings and internal structural parts of home appliances can be manufactured using GMT compression molding, which provides good electrical insulation and durability.
- Sporting Goods: In the manufacturing of sports equipment such as skis, skateboards, and boat hulls, GMT materials provide the necessary strength and light weight to ensure high product performance.
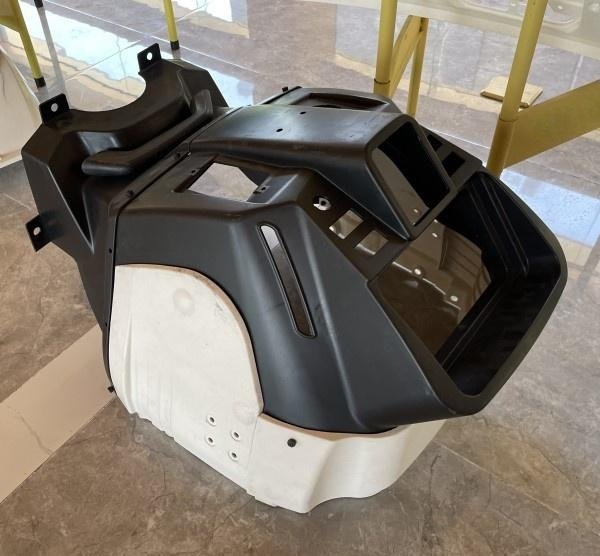

V. Challenges and Future Trends of GMT Compression Molding
Although GMT compression molding offers significant advantages in multiple fields, it also faces some technical challenges:
- Material Cost: Compared to traditional plastic materials, the cost of GMT materials is higher, which limits their widespread use in some low-cost applications.
- Recyclability Issues: The recycling of GMT materials remains a challenge. With increasing environmental requirements, more innovation will be needed in the future to enhance their recyclability.
- Technical Requirements: GMT compression molding requires high-precision molding equipment, and the technical requirements for equipment maintenance and operation are high.
In the future, with advancements in material science, the performance and production efficiency of GMT compression molding will be further improved. Concurrently, with the promotion of environmental policies, technological innovation will also lead to breakthroughs in sustainability.
VI. Conclusion
As a new type of high-performance material forming technology, GMT compression molding, with its excellent advantages of being lightweight, high-strength, and corrosion-resistant, has become one of the important technologies in fields such as automotive, aerospace, and construction. With the continuous advancement of production technology, GMT compression molding will be applied in more industries, driving the innovative development of global manufacturing.

-3-768x491.jpg)